The capability of the Express Search is to allow Tactical and Analytical LInX users to perform an express structured search that contains only the most commonly used fields. The results of a search will be presented in the same manner as other LInX structured search results.
Tactical and Analytical LInX users can access Express Search either from the Query Tools title page, or from the menu bar located along the left side of the screen.

The Express Search page allows users to enter search criteria that can be used to generate search results. This page also provides the capability to Save/Watch and Load search queries.
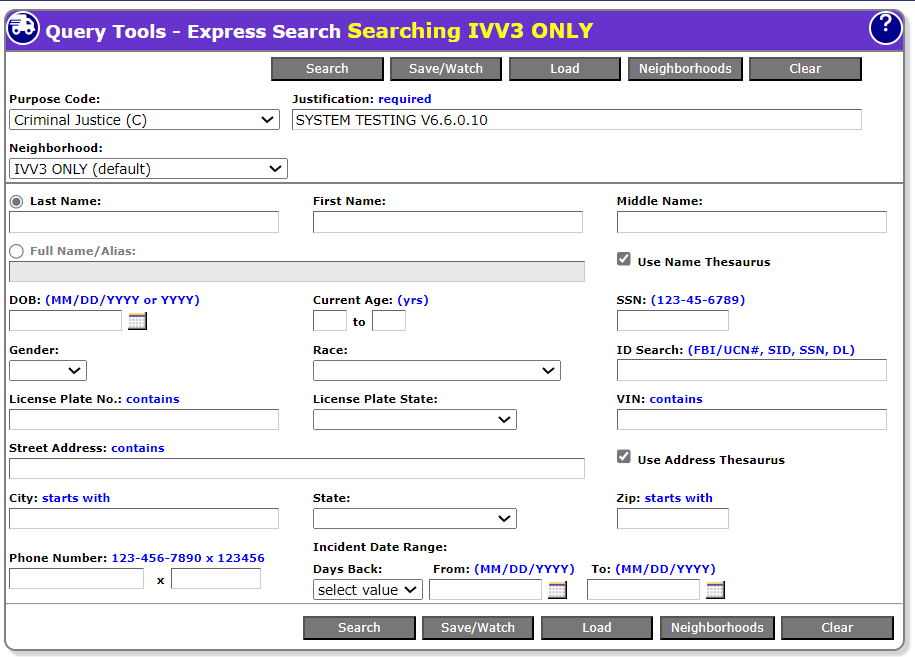
The most common search criteria related to people, vehicles, addresses, incident characteristics, and/or phone numbers can be entered into the appropriate fields shown on the Express Search screen. When the Express Search screen is used to perform a query, the search process will look for names associated with incidents that meet ALL of the criteria entered in the various search characteristics categories.
Note: The Express Search screen contains the same search fields for both Tactical and Analytical searches. The only significant difference is the result set; specifically, the ability of Analytical users to view the contents of the Narrative tab for the results of the search. The Narrative tab is not available for Tactical-only users.
Express search fields
The following fields are used as the search criteria for Express Search:
Ø Purpose Code (defaulted to Criminal Justice (C))
Ø Justification (highlighted in yellow if required)
Ø Last Name
Ø First Name
Ø Middle Name
Ø Full Name/Alias
Ø Name Thesaurus [check-box]
Ø DOB or Year of Birth
Ø Current Age or Current Age Range
Ø SSN
Ø Gender [drop-down list]
Ø Race [drop-down list]
Ø ID Search (FBI, UCN, SID, SSN, DL)
Ø License Plate No.
Ø License Plate State: [drop-down list]
Ø VIN
Ø Street Address [Person or Event]
Ø Address Thesaurus [check-box]
Ø City
Ø State [drop-down list]
Ø Zip
Ø Phone Number
Ø Incident Start Date (mm/dd/yyyy)
Ø Incident End Date (mm/dd/yyyy)
Ø Map Selection [(Change Map Region...) link]
Ø Neighborhood (drop-down selector)
Note: The ID field is not to be considered when searching for NCIS data.
Exact and thesaurus Search Options
There are two different levels of complexity available for users to conduct searches, depending on the field(s) being searched. The options available are:
Exact Search: limits the search results to those records that are an exact match to the search criteria. Results will only be returned if they meet all the criteria entered in the various search characteristics categories. Results will be returned for exact spelling or numerical matches.
Exact Searches may be conducted for Name and/or Address queries. Exact Search is the default setting, and will be conducted for Name and/or Address queries unless the respective Thesaurus check-boxes are selected.
Thesaurus Search: uses a static LInX thesaurus index to expand the search results to include structured records that contain terms that are grouped together according to similarity of meaning to the search term(s), in addition to those records that contain exact matching terms to the search criteria. Results will be returned for exact spelling or numerical matches, and related terms.
Thesaurus Searches may be conducted for Name and/or Address queries.
Examples of Thesaurus entries using the Person Full Name index include:
William - Will, Willie, Bill, Billy
Steven - Stephen, Steve, Steph
Kenneth - Ken, Kenny
Examples of Thesaurus entries using the Full Street Address index include:
Street - St, Str, Strt
Road - Rd
Avenue - Av, Ave
1st - First
To conduct thesaurus Name searches, click the Use Name Thesaurus check-box to the right of the Full Name/Alias field to select the option.
![]()
To conduct thesaurus Address searches, click the Use Address Thesaurus check-box to the right of the Street Address field to select the option.
![]()
The Use Name Thesaurus and Use Address Thesaurus options may be selected from the Express Search query screen. The desired default search types can also be set by the user on the Set Preferences screen, under My LInX.
The following chart compares Exact Search and Thesaurus Search.
|
|
Exact Search |
Thesaurus Search |
|
Full Name/Alias Field |
LInX will identify structured records containing a full name/alias that exactly matches the user-entered search term(s). |
LInX will identify structured records containing a full name/alias that match exactly the user-entered search term(s) or match entries found in a static LInX thesaurus index. |
|
First Name, Middle Name, Last Name Fields |
LInX will identify structured records containing first name, middle name, last name fields that exactly match the user-entered search term(s). |
LInX will identify structured records containing first name, middle name, last name fields that exactly match the user-entered search term(s) or match entries found in a static LInX thesaurus index. |
|
Full Name/Alias Field Combined with Other Fields |
LInX will identify structured records containing a full name/alias that exactly match the user-entered search term(s) and that also contain an exact match for the user-entered search term(s) in the other field(s). |
LInX will identify structured records containing a full name/alias that exactly match the user-entered search term(s) or match entries found in a static LInX thesaurus index, and that also contain an exact match for the user-entered search term(s) in the other field(s). |
|
First Name, Middle Name, Last Name Fields Combined with Other Fields |
LInX will identify structured records containing first name, middle name, last name fields that exactly match the user-entered search term(s) and that also contain an exact match for the user-entered search term(s) in the other field(s). |
LInX will identify structured records containing first name, middle name, last name fields that exactly match the user-entered search term(s) or match entries found in a static LInX thesaurus index and that also contain an exact match for the user-entered search term(s) in the other field(s). |
Use of Wildcards
Exact Search can also be used with wildcards to expand or speed up the search while still limiting it to the search criteria entered by the user:
Ø A wildcard (%) can be used in an exact search to bring up additional records that reflect the criteria including the wildcard, such as ”Doe, J%” for all individuals with the last name of "Doe" and a first name beginning with the letter "J".
Ø If the search involves alphanumerical values, such as a partial license plate, the location of the wildcard within the number sequence will determine the results that are returned (see following table).
Ø Wildcards can be used to speed up a search by inserting a wildcard after the search criteria, which has the effect of limiting the search results that begin with the criteria instead of containing the criteria anywhere within the record. Using the wildcard in this way may speed up the search if time is a concern and the possible number of candidate returns is large, such as Street or City names.
Ø Wildcards can also be used in Driver’s License Numbers, Street Names, City Names, Street Numbers, and Social Security Numbers.
The following chart provides examples of the results returned when using wildcards in Exact Search queries:
|
Exact Search Wildcard Placement Examples |
Results |
|
Names (People, Places) |
|
|
J% Doe |
All individuals with first names starting with ”J” and last name of ”Doe” (and any aliases on records as the letter ”J”). |
|
Cent% Street |
Street Names starting with ”Cent”, such as Central, Center, or Centre. |
|
Oak% Street (wildcard used to speed results) |
Street Names of ”Oak”, limiting the search to Street Names of Oak, or starting with the word Oak, such as Oakdale. |
|
Numbers and Alphanumeric Sequences |
|
|
%123 |
Sequences ending in ”123” and sequences with ”123” in the middle, or results of ”123”, if that is the entire record (such as ”123 Main Street”). |
|
123% |
Sequences starting with ”123”. |
|
%12%3% |
Sequences with known characters in this order. |
|
123 (no wildcards) |
Returns results of ”123” alone or "123" anywhere in the sequence, in any field that is noted with the word ”contains”. |
Searching Phone Numbers
Query on a phone number by entering search criteria in the phone number fields and then selecting the Search button:
Ø Main Phone Number (Area Code, Prefix/Suffix)
Ø Phone Extension
There are two fields that are associated with the phone number field (as shown below).
![]()
The single field for the main phone number allows for cut/paste operations from another document into LInX. Note that extensions are rarely captured in an RMS.
Phone Numbers may be entered in a variety of formats, and the number will be parsed into component fields automatically. The following formats are supported:
(123)123-1234
123-123-1234
123.123.1234
1231231234
Entry Rules & Error Messages
There are several rules associated with the entry of phone number search criteria:
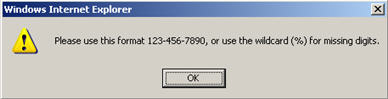
7 Digits Required:
If a prefix/suffix is entered without using a wildcard (%), as shown in the following example, then the complete 7 digit phone number MUST be provided.
![]()
The following message will appear if you do not meet entry criteria.
Wildcards Allowed:
LInX DOES allow the use of the wildcard (%) character, which is one of the most effective approaches for querying phone numbers. The wildcard (%) may be prepended, appended, or placed on both sides of a partial number, as shown in the example below.
![]()
Note that when one or more wildcards are used, dashes are automatically inserted to parse the Phone Number into component fields.
|
Tip: To get the maximum results for partial phone numbers, use the wildcard (%) on the left, right, or both sides of the partial number.
Tip: The area code is often omitted from RMS data. It is not required for a phone number search -- leave it out in order to get maximum results on a search for partial phone numbers. |
Search only last 2 years of data
An initial query may be limited to search data for the most recent 2 years, by clicking on the Last 2 years hyperlink next to the Incident Date Range on the query screen. Selecting this option will automatically pre-populate the Date Range fields, extending back 2 years from the current system date.
When the Date Range fields are pre-populated to search the last 2 years of data, clicking on the Clear hyperlink will remove the limitation, and allow searching of older data.
![]()
![]()
Note: if the Date Range is manually entered, the Last 2 years link will remain and the Clear link will not be displayed.
The default Express Search setting is to search the designated default neighborhood, as defined by the regional system administrator. Typically this would include all local contributing agencies; meaning that the search includes all data in the data warehouse from all local sources.
The Neighborhood drop-down selector allows a user to access and select other existing System Defined and User Defined neighborhoods.
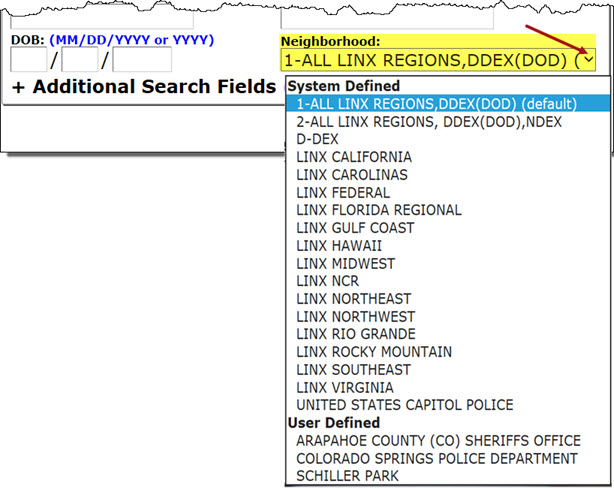
To select an existing neighborhood from the Neighborhood drop-down menu, just click on the desired neighborhood. The neighborhood field will automatically update with the name of the selected neighborhood.
The Neighborhood button allows a user to access the Neighborhood Selection menu and select one or more agencies, sites, and/or Partner systems against which to conduct a search. The results will be filtered to reflect only the data from the selected source(s) when the user limits the search to one or more source agencies, rather than all agencies.

Selecting a Neighborhood:
When the Neighborhood button is selected, the Neighborhood Selection menu and a description of the screen functionality are displayed. Additional help for Neighborhood Selection can be found within the Neighborhood Selection functionality by clicking on the Online Help button [![]() ] located in the upper right-hand corner of the Neighborhood Selection screen.
] located in the upper right-hand corner of the Neighborhood Selection screen.
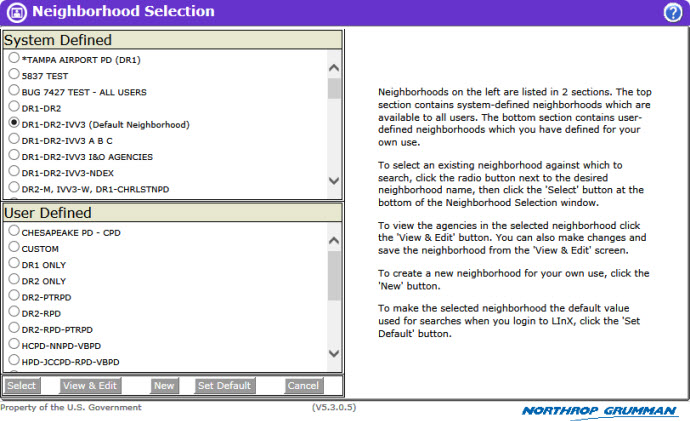
Selection Status:
The text appearing on the Query Tools - Express Search banner provides the user with the selection status. If there are no neighborhoods listed, or no neighborhood has been identified as the ”default” neighborhood, the local agencies of the current LInX system, plus whichever remote system(s) that may be included as a default by the Regional Administrator, will be the default agency source criteria for all searches.

In addition to the banner, the text appearing to the left, below the navigation menu also provides the user with the neighborhood selection status. If there are no neighborhoods listed, or no neighborhood has been identified as the ”default” neighborhood, the local agencies of the current LInX system, plus whichever remote system(s) that may be included as a default by the Regional Administrator, will be the default agency source criteria for all searches.
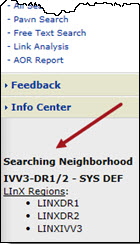
When a different neighborhood selection is made, the selection status changes to reflect the name of the newly-selected neighborhood.
The Map Selection functionality provides the user with the ability to search a specified geographic area. When the (Change Map Region …) link is selected, the Map Selection screen opens in a separate window.
Selection Status:
The text appearing above the (Change Map Region ...) link on the query screen provides the user with the selection status, which corresponds to what is selected in the Neighborhood Selection menu. If no neighborhood is selected under the Neighborhood Selection menu, then the system default will be used, and no map regions will be specified.
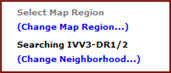
When a Map Region is selected, the Neighborhood selection status will change to CUSTOM. The neighborhood will automatically be modified to include the selected regions/agencies. The neighborhood can then be modified further through the Neighborhood Selection menu.
Mousing over the Map Regions label (directly above the Change Map Region link) will display a pop-up message containing the name(s) of the map region(s) selected.

Additional help for Map Selection can be found within the Neighborhood Selection functionality by clicking on the Online Help button [![]() ] located in the upper right-hand corner of the Neighborhood Selection screen.
] located in the upper right-hand corner of the Neighborhood Selection screen.
The N-DEx portal search requires users to enter a search purpose, (e.g., Criminal Justice, Criminal Justice Employment, or Administrative File Maintenance) in order to perform a query. Depending on the purpose of the query, certain data may be omitted from the results returned to the user. This enhancement allows LInX to maintain its CSP compliance.
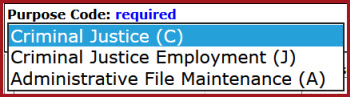
The Purpose Code is required in LInX and will be defaulted to Criminal Justice (C) for all search types, but may be changed, as needed. Purpose Code will remain persistent throughout the current session for any LInX search, unless changed during the session.
This function allows Tactical and Analytical LInX users the ability to enter the reason a search is being conducted. This field is located at the top of each query screen. The field is automatically highlighted in yellow, contains a hint identifying the type of information that should be included when entering a justification, and is required if one or more agencies in the selected neighborhood require a justification in order to search their data.
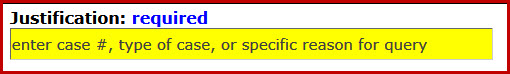
If a Purpose Code of Criminal Justice Employment (J) is selected, the system will default the Justification to "Employment". When the Purpose Code is changed to Criminal Justice (C) or Administrative File Maintenance (A), the Justification field is cleared and must be entered/re-entered.
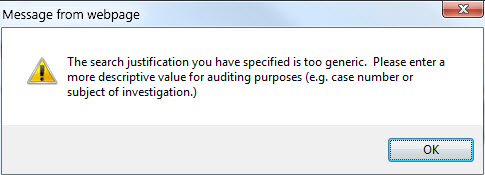
If the justification entered is too generic, a pop-up message will be received advising the user to enter a more descriptive value.
Justification will remain persistent throughout the current session, for any LInX search, unless changed during the session.
Express Search Tips
|
Tip: Less is better! Starting with just Last Name and First Name is usually the best approach, as it will result in the largest results set.
To refine the search, adding the DOB is often the best choice to add to the search criteria. However, matches will only improve if the additional identifiers match the contents of the original records in the database.
Tip: Use wildcards (%) for name queries where the person may have more than three names. The wildcard can be placed before, and/or after the Last Name. It may be valuable to conduct separate searches of both the Middle and Last Name fields.
Tip: Consider reversing the names in a search. Some cultures actually use the Last Name as a First Name.
Tip: Use the Full Name/Alias search field when only one portion of a name is known or when searching for a "street name" or a single name alias (e.g., "Killer", "Peanut", "Catfish", etc.). This will search the Last, First, Middle, and Alias name fields.
Tip: Because of various spellings of names, a wildcard (%) can be used if the correct spelling of a person's name is unknown (e.g., Gonzale% to retrieve Gonzales and Gonzalez).
Tip: Searches by Social Security Number may assist with the identification of persons who have changed their name (legally or otherwise). |
|
Tip: When a query requires a "wide-open" data search (e.g., White, Female, DOB), such as in a Cold Case investigation:
1. Set the Search Results Increment under My LInX/Set Preferences to 1000 to bring back the maximum result set 2. If running the query from All Search, ensure Also Search Free Text is disabled 3. Issue the search with just one attribute (e.g., DOB).
The return on both the initial results and subsequent "Get More" results will be faster.
When all available results have been retrieved/merged (Get More/Merge Results), filter on any additional attributes to narrow the results further, as needed (e.g., White, Female). |
Analytical and Tactical LInX users have the ability to save queries, watch saved queries for new information, and load saved queries.
Saved Queries
Queries may be saved directly from the Query screen by clicking on the Save/Watch button, which will display a Save and Watch Query screen.
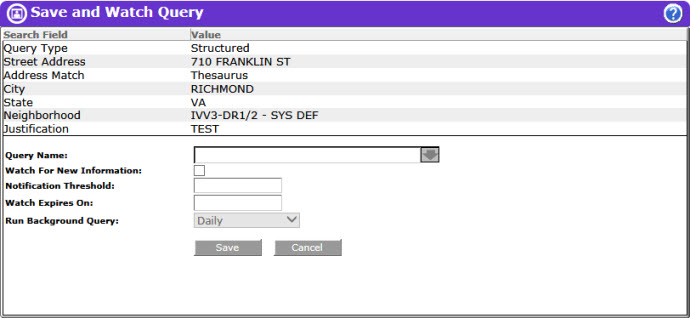
The top portion of the Save and Watch Query screen contains the search parameters and criteria that will be saved.
Enter a name in the Query Name field, and click the Save button. The user is returned to the previous screen and a pop-up message is displayed stating that the query has been saved. Click OK to close the message box. Saved queries may be viewed and managed from My LInX/Manage Watch List.
Clicking the Cancel button will return the user to the previous screen without saving the query.
Watched Queries
Users may also set watches on selected saved queries to monitor for new information, get notifications when new information is available, and view the new information. Watched queries that search other LInX and Partner systems can be created.
To watch an entity, a query must contain at least one of the following sets of criteria:
• First Name + Last Name (with/without Thesaurus)
• SSN
• Misc ID
• Full Name
• Occupation
• Tag Number
• VIN
• Street Address + City + State
• Phone Number Prefix + Suffix
• Property Serial Number
Queries can be configured to be watched directly from the Query screen without first running the query by clicking on the Save/Watch button, which will display a Save and Watch Query screen.
After entering a name in the Query Name field, click the Watch For New Information check-box in the Save and Watch Query window to select it. The Watch Expires On field is automatically populated with a date 90 days from the current date.
NOTE: The Notification Threshold field identifies the most recent record available in the system for a watched query, and will remain blank when configuring a watch from a Query screen. It is recommended that watches be configured from a Structured Results or Query History screen, so the Notification Threshold can be set. If a query returns no results, a watched query for that search criteria can still be configured from the Query screen.
Next, click the down arrow at the end of the Run Background Query field to select the frequency of the background search (Daily, Every Other Day, or Weekly). The default setting is Daily.
After all the desired settings are configured, click the Save button. The user is returned to the previous screen and a pop-up message is displayed stating that the query has been saved. Click OK to close the message box. Watched queries may be viewed and managed from My LInX/Manage Watch List.
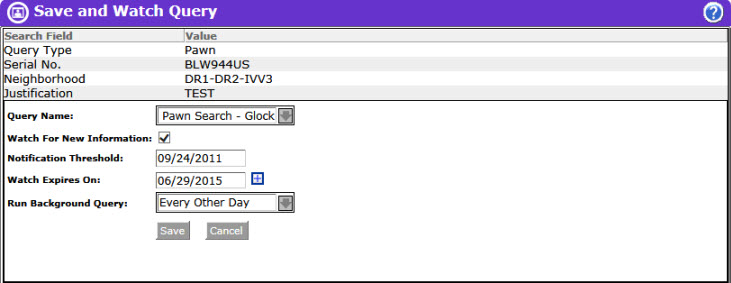
Clicking the Cancel button instead of Save will return the user to the previous screen without saving/watching the query.
Any attempt to watch a query that does not meet the minimum requirements will result in a pop-up message stating ”Query has been saved but does not meet the minimum requirement for a watch query.” The saved query can be viewed under My LInX/Manage Watch List below any watched queries.
When all the information to be used in the query has been entered, and the source of information selected, clicking on the Search button will begin the search process.

The Clear button, located at the bottom of the search screen, will clear all the fields in the query screen, with the exception of the Justification field, without having to leave the query screen.
Load Saved Queries
Users may load any of their saved queries directly from the Query screen by clicking the Load button, which will open a Query Selection menu in a separate window.
To view the search criteria for a saved query mouse-over the selected query name for a moment. The LInX system will retrieve the search criteria and display the query details to the user in a pop-up description box.
To load a query, ensure that the radio button for the desired query is selected, and then click the Load button. A pop-up message stating ”Requested query loaded” is displayed. Click the OK button to close the pop-up message.
The query screen is re-displayed and populated with the search criteria from the selected saved query. Click the Search button to run the query.
Clicking the Cancel button from the Query Selection window will close the window and return the user to the Query screen without loading any data.
Tactical and Analytical users should contact their System Administrator or Agency Administrator when they are having problems accessing or using LInX. Only System Administrators are authorized to contact the LInX Help Desk.